Why STEM Education in Australia
Why STEM Education in Australia
Dr. Heath Kirby-Miller | December 25, 2021
How can parents, industry and schools help progress STEM Education in Australia?
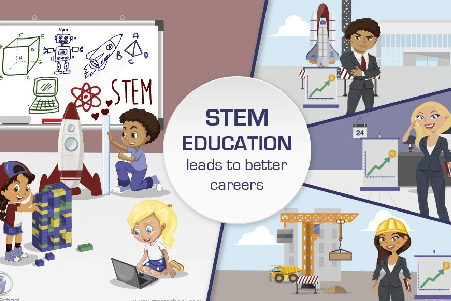
STEM refers to Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths. STEAM includes Arts as well. Creativity is an essential element of STEM.
In November 2021, according to the Department of Education, Skills and Employment (DESE):
“Australian students don’t understand the importance of STEM, or STEM career opportunities, until it’s too late.”
Parents of school going children should (must) take an interest in STEM as a future valuable skill for their children. The investment now may seem expensive, but it will help to position children for future job opportunities. Without STEM skills, it is possible that many STEM opportunities would not be available to children who were not given the opportunity to learn and understand STEM. To help children explore STEM, there is a lot of online STEM-content, including on streaming service Netflix.
Role of Australian industry in the growth of STEM education in Australia.
What is the role of Australian industry in the growth of STEM education in Australia? Australian industry is concerned about skills shortages and recruitment of qualified STEM candidates. Changes in the global economy mean that workers require skills for emerging industries. Applying STEM skills and knowledge can deliver benefits, including the below:
- new products and technologies
- more efficient services and systems
- higher quality health care
- enhanced natural resource management
- new ways to respond to environmental change
- progress on tackling national and global challenges
- better decision-making in governments and industry
(Source: Department of Industry, 2021)
Why STEM Education in Australia
The Australian industries assured to benefit from STEM include advanced manufacturing, health, energy, information and communication technology and agribusiness. These industries should seek to work together, and with other STEM-stakeholders, to build the pipeline of STEM-qualified candidates in Australia.
An Australian-based STEM qualified workforce should be industry’s end goal, knowing that all industry players will benefit from a local STEM-ready talent-pool.
Here, the Australian government, and particularly, universities can collaborate to provide STEM courses to university students. Private education businesses also have a role to play too. So too do industry and employer groups.
What is the role of Australian schools to progress STEM education in Australia? Broadly, providing Australian children with opportunities to engage in learning STEM. Any exposure to STEM would seem useful. Workshops allow both children and teachers to explore exciting possibilities. Longer term, STEM can be integrated into the Australian curriculum, particularly at secondary-school level, and aligned to ensure learning outcomes that contribute (in even a small way) to industry’s goals.
Then, universities can promote more advanced STEM to help in the longer-term objective for industry to be able to hire newly-qualified engineering graduates.
No matter who plays what role though, the central argument around advancing STEM is accessibility to all. Girls, women and those disadvantaged in the community (including those in regional and remote areas of Australia) should be more involved in STEM initiatives.
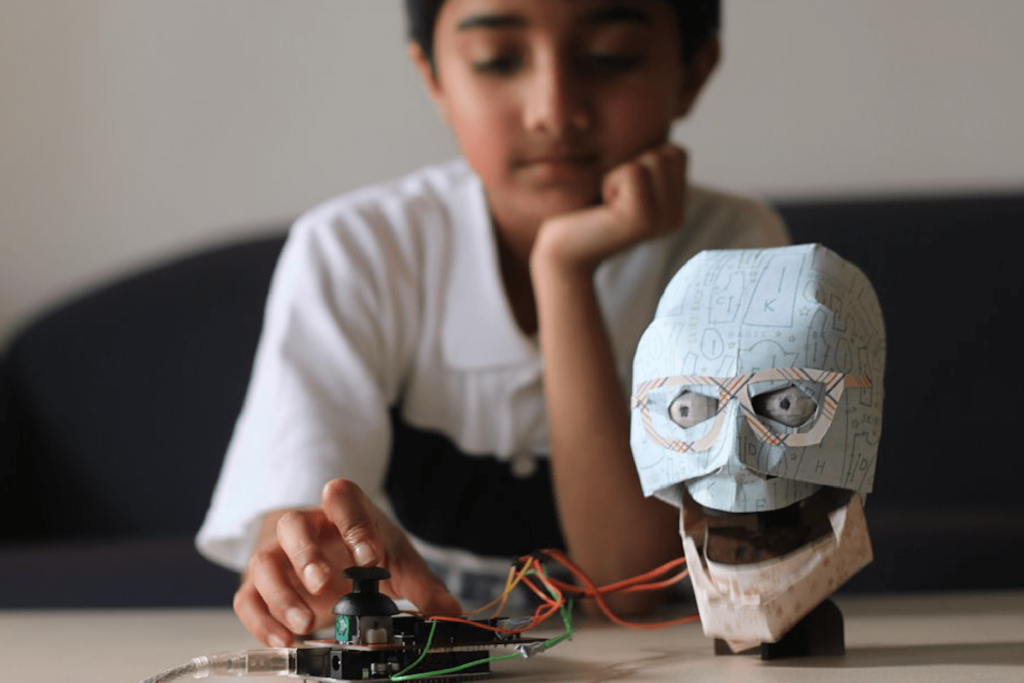
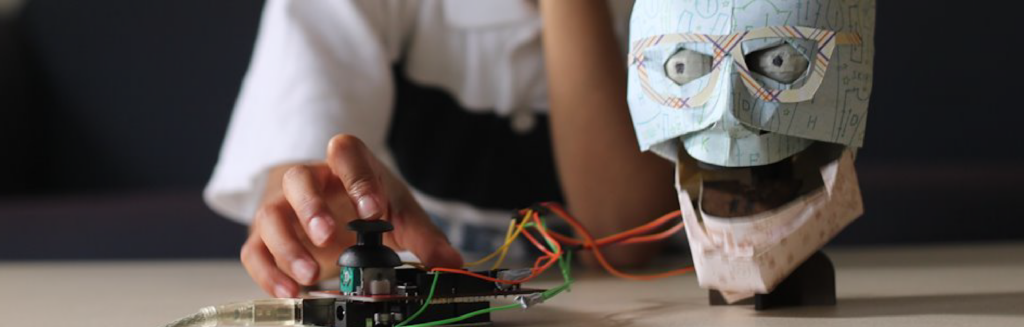
Mechatron Robotics Australia offers a range of STEM-related content for children aged 6-16, and for adults. Content can be delivered online, in small groups (4-8 students, typically), and face to face in engaging workshops and classes.
REFERENCES
Australian Academy of Technology & Engineering. Investing in a post-COVID 19
tech boom.
Retrieved 25 November 2021 from
https://www.atse.org.au/news-and-events/article/6706/
Australian Government. (2021). Why is STEM important?
Retrieved 25 November 2021 from https://www.dese.gov.au/australian
Curriculum/national-stem-education-resources-toolkit/introductory-
Material/why-stem-important
Department of Industry. (2021). Science, technology, engineering and mathematics
(STEM). Retrieved 25 November 2021 from
https://www.industry.gov.au/policies-and-initiatives/science-technology-
engineering-and-mathematics-stem
The Australian Industry Group. (2021). Increasing Australia’s STEM capabilities amid
COVID-19. Retrieved 25 November 2021 from
https://www.aigroup.com.au/news/blogs/2020/increasing-australias-stem-
capabilities-amid-covid-19/